The Skin’s Mechanisms of Regeneration
The skin has three layers consisting of the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis.
The epidermis, which is the outermost layer of the skin, is continually renewed by the production of new cells.
As the cells in the basal layer divide and differentiate, they lose their internal structure and move up toward the surface, where the remaining lipid membrane undergoes keratinization and eventually sheds.
Healthy skin renews itself and “turns over” about every 28 days.
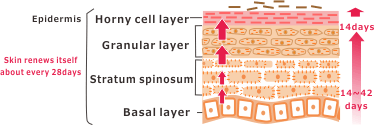

As the skin repeats the cycle of renewal, the cells near the surface of the skin are subject to damage from ultraviolet exposure or scars, but the internal structure remains protected and healthy.
But・・・
Serious damage due to ultraviolet exposure and scars causes the turnover cycle to accelerate or decelerate which in turn impedes the regeneration of healthy skin.
Factors that could contribute to the disruption of skin turnover:
◆Aging
With aging, the function of the basal layer decreases and turnover slows down.
◆Ultraviolet exposure and scars
When the skin suffers damage from ultraviolet exposure or scars,
the skin attempts to compensate by accelerating turnover.
And so on
When these factors cause turnover to accelerate or decelerate…
The skin is affected in the following ways↓↓


This shows that a regular turnover cycle is important to maintain healthy skin.
Then, what is the key to normalizing turnover?
The answer is…
Skin care!
It’s important to keep in mind that the skin needs sebum in order to maintain its barrier function.
Of course,
we also need to make adjustments in our lifestyles to prevent such conditions as:
- sleep deprivation
- poor blood circulation
- malnutrition.
Le Chêne soap is made using a process called superfatting to increase the fatty acid composition.
This helps to prevent dry skin which regular soap tends to cause.

